Field notes
What's the deal with HTTPS?
HTTPS is designed to secure communication between parties by establishing encrypted connection. It allows to encrypt the messages so even if they’re intercepted nobody would be able to read them or modify unless they have a pair of Public/Private keys.
This is achieved by utilizing asymetric encryption keys.
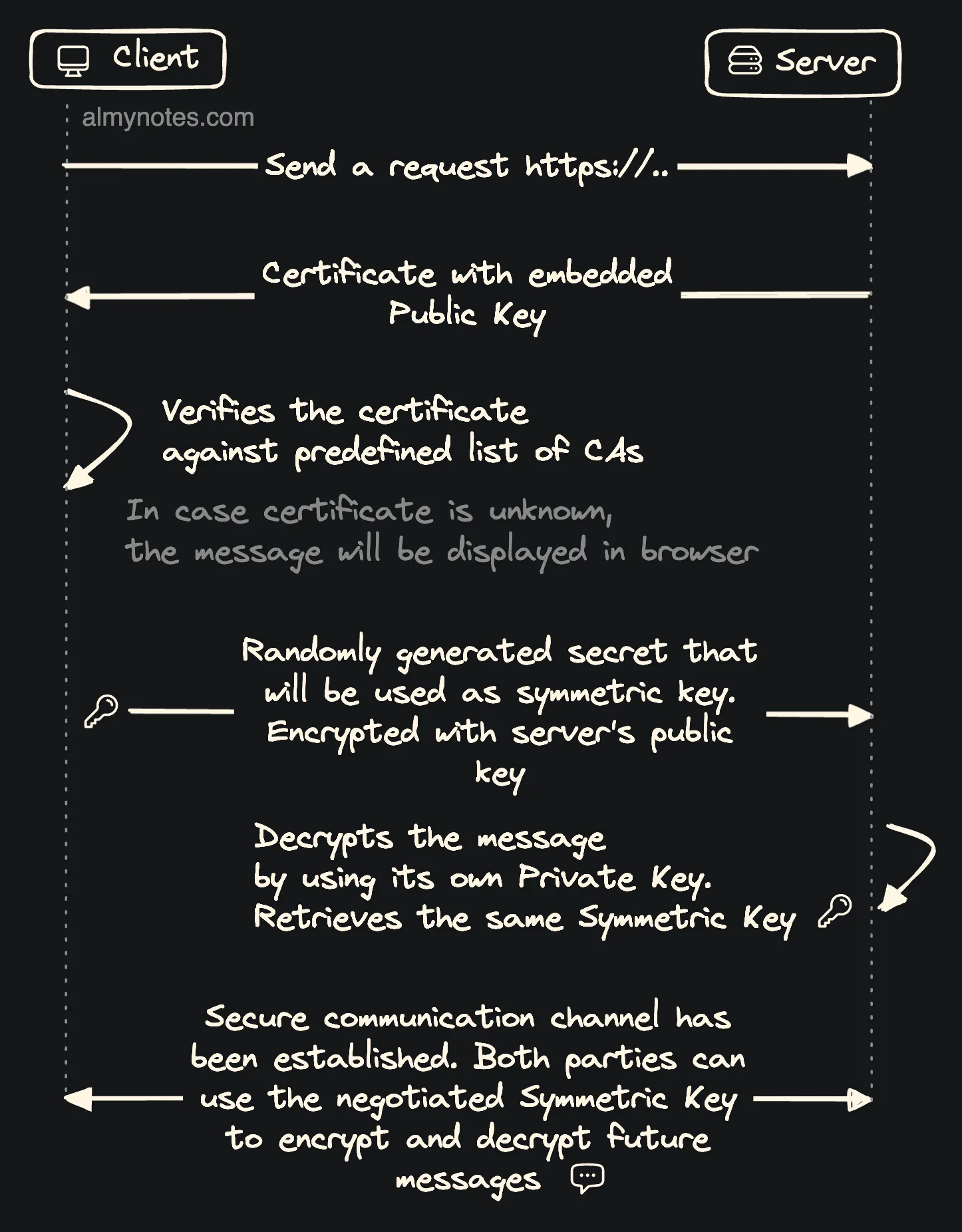
- The process starts with a handshake. Client sends
ClientHellomessage when it wants to initiate the communication. The message contains metadata with preffered SSL version, cipher suites etc. Server choses preffered settings and sendsServerHellomessage in response. It contains similar set of data. - Client and Server are exchanging with their digital certificates. Among other information certificate includes public key and the information about its issuer. For simplicities sake in this step we can focus on Server. It sends certificate to prove its identity to the Client. So the client knows that it communicates to the Server that is legit.
- Client verifies the cetrificate to be sure it’s issued by one of the trusted Certicication Authorities. This is important part as client has to be sure that certificate was not tampered while it was in transit from server. Otherwise somebody could have intercepted request and exchanged the certificate. If we’re talking about secure applications server can also check client’s identity to be sure it can trust it.
- Client generates a random key, encrypts it with Server’s public key and sends it to Server. The entire message is signed with Client’s public key. When received the Server verifies the message, decrypts the key by using its own Private Key. At this time both parties have the same key. This is called symetric encryption key. It will be used for encrypting and decrypting all the messages in further communication. Utilizing symetric key requires less computational power and allows to save some resources.
The important part in the above algorithm is played by Certification Authority (CA). Without CA it wouldn’t be possible to negotiate symetric key as parties wouldn’t know if they could trust to certificates they receive. Anybody could intercept the requests and edit the certificates. But having CA in place allows to verify if Certificate is legit. The browser itself is coming with predefined list of CAs that can be used to verify legitimacy of the certificates. On top of that the browser also has a list of trusted certificates controlled by secure centralized group. If needed you can extend this list on your own.
Digital Certificate
Certificate is a file that contains information about server owning it. It cosists of the following blocks:
- Subject - name of the entity it was issued to
- Validity period
- Public key - opposite to Private Key this one distributed publicly with the certificate. Private Key stored securely on the server
- Digital signature - used to verify authenticity of the certificate. Certification Authority that issued this certificate needs to be trusted by Client. If that’s the case Client can use public key of CA to verify if Digital Signature is valid.
There are different types of certificates:
- PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail) - Files with extension
.pem. Contains base64 encoded certificate between— — - BEGIN CERTIFICATE — — —and— — - END CERTIFICATE — — - - PKCS (Public-key cryptography standards ) - Files with extensions
.p12,.p8,.p7betc. They contain public and private keys in the same file. - DER (Distinguished Encoding Rules) - Files with extensions
.cer,.crt,.der. Contains binary encoded certificate.
SSL Certificate Pinning
This is the process of associating a host with its certificate or public key. It’s used to verify that communication with host stays secure. By using SSL pinning you make your application to trust predefined certificates and public keys.
So if you distribute the application you need to embed certificate into the application bundle. Then at the runtime application would rely on this certificate to compare it with what comes from server.
Public Key Pinning
In practical terms it means you’re retrieving public key from the certificate as a string. Then this string is passed into your application as configuration parameter. Then at runtime application would rely on this string to compare it with public key coming from server in Certificate.
The benefit of pinning public key over pinning certificate is that you don’t need to re-distribute application every time certificate changes. As certificate rotation happens public key doesn’t change so applications using it wouldn’t need to be re-distributed. The downside though is that you need to extract public key from certificate coming from server every time the connection is established.